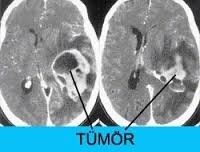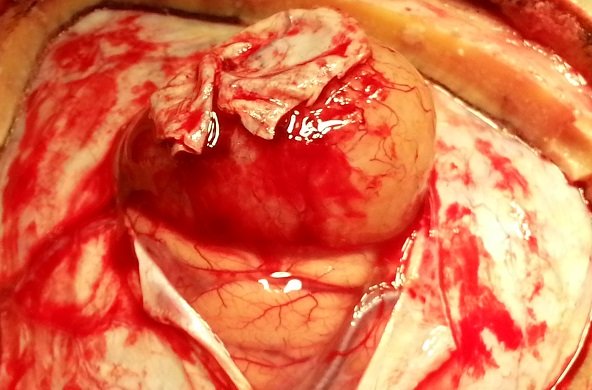
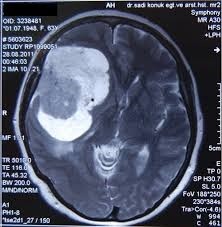
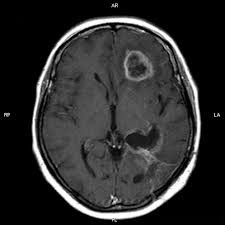
Structures that become malignant and benign as a result of abnormal growth of normal cells in the brain are characterized as brain tumors. Brain tumors are seen at all ages, including newborns.
After middle age, especially in the majority of cancer patients, a tumor may occur in the brain with the spread of cancer. The resulting mass causes an increase in intracranial pressure and starts to put pressure on the brain and shows some negative symptoms.
Early diagnosis of brain tumors often affects the patient’s life and quality of life.
The brain loses its normal structure under pressure and becomes unable to perform its functions, and the following symptoms are mainly observed:
1- Headache
2- Epilepsy-like fainting
3- Partial paralysis in some parts of the body
4- Severe vomiting
5- Loss of some physical abilities
6- Personality disorders
Headache, Only 60% of patients with brain tumors have a headache. Our patients state that the pain has emerged in the last few months and is getting worse and worse.
It is important that nausea is present with vomiting, Headache and especially if it has been present for several days or weeks. However, the presence of headache and vomiting for a long time suggests migraine.
Double vision and blurred vision, Double vision with or without headache, blurred vision, decreased vision are the first signs of brain tumors.
Weakness, clumsiness, instability in the arms and legs, numbness in the right or left half of the body that have appeared recently, weakness in the hands, numbness, clumsiness can be seen. “Drunken gait” and “unsteadiness” when walking can be a sign of a cerebellum tumor.
Speech disorder, inability to speak, difficulty in understanding, incorrect word expressions while talking or drunken speech may also be the first sign of brain tumors.
Epilepsy, involuntary convulsions with or without loss of consciousness, feeling bad like a panic attack can be a type of epilepsy. Such seizures, especially after the age of 20, should be investigated until proven otherwise, considering that they are related to a brain tumor.
It is possible to divide brain tumors into two main lines…
Brain tumors are generally classified as primary or secondary, and they are (usually) those that start anywhere in the body and metastasize to the brain, and those that occur in the brain. Brain cancers, which are more common under the age of 9 and over the age of 55, are more common in Caucasians and men.
1- Benign tumors: They have a slow reproduction rate. In addition, they can be easily separated from the brain tissue and all or almost all of them can be removed. Therefore, the postoperative results are very good. However, even if the tumor is benign, if it is located in sensitive areas of the brain, the results are unfortunately not satisfactory.
2- Malignant tumors: They reproduce very quickly. They are in the form of mud. Therefore, they cannot be completely removed by surgery. After the surgery, they continue to grow again in a certain period of time and continue to put pressure on the brain. It is possible to classify malignant tumors according to their reproductive rate. There are tumors that give a chance to live for 5-6 years after surgery, as well as tumors that regenerate in 5-6 months and cause the death of the patient.
Treatment of brain tumors is surgery. All tumors, whether benign or malignant, are treated surgically. However, in some cases, surgery may not be possible. If the tumor is located in some vital areas of the brain that are very sensitive, touching these areas is life-threatening, and the tumor can be left in place. In this case, only radiation therapy and drug therapy (chemotherapy) can be applied.
Tumors in other parts of the body can spread to the brain. This is called metastasis. Especially lung cancers can spread to the brain and are malignant tumors. Even if surgical intervention is performed, the results are not satisfactory. In some cases, even surgery may not be performed if there are several focal spreads. The patient is taken to chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
CLASSIFICATION OF BRAIN TUMORS
Pituitary adenomas
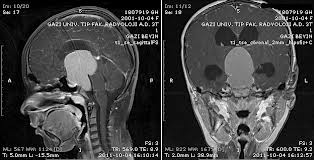
Pituitary adenomas are divided into two main groups as those that secrete hormones and those that do not secrete hormones. Those who secrete hormones usually give symptoms depending on the hormone they secrete. Adenomas that do not secrete hormones do not give any symptoms for a long time. However, they cause visual disturbances by pressing on the optic nerve. Hormone disorders, menstrual irregularities or absence, milk coming from the breast, excessive fatness, rapid height growth, are the symptoms of growth hormone disorders in the hands, feet and chin, and a doctor should be consulted. If the tumor size increases too much, it increases intracranial pressure and causes general symptoms such as headache, nausea and vomiting.
MENENGIAL TUMORS
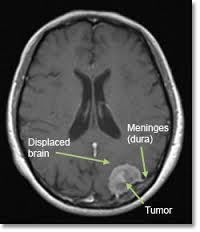
Meningiomas generally enlarge, causing increased intracranial pressure and headache, nausea and vomiting. Epilepsy (Sara) seizure can also be seen. In addition, these tumors give symptoms according to their localization. Those located near the optic nerve (Visual nerve) cause visual impairment, while those close to the movement-related brain area can cause paralysis. For this reason, necessary examinations should be made in disorders of brain functions
METASTATIC TUMORS
Metastatic tumors are tumors that occur due to the spread of tumors in other parts of the body to the brain tissue. These tumors show symptoms by increasing intracranial pressure and/or by causing damage to the nervous system depending on the location. In general, such jumps may be the first sign of tumors. These tumors form extensive edema that can also be visualized radiologically.
CORNER (PONTOCEREBELLAR) TUMORS
These tumors are tumors located in a region of the brain tissue. Auditory nerve tumor (acoustic neuroma) is the most common tumor. In addition, meningioma (Cerebral Tumor) and epidermoid tumors are also encountered. In addition to the general symptoms of brain tumors, hearing and balance disorders are also observed in tumors of this region. When these tumors are caught in small size, hearing can be preserved. If the tumor is very large, hearing may not be preserved and the Facial Nerve may also be affected.
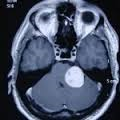
GLIAL (BRAIN TISSUE) TUMORS
These tumors are usually malignant and grow within the brain tissue. Symptoms are general symptoms. Again, they give symptoms depending on the regions where they settle. Epilepsy (Sara seizure) may occur as the first symptom in some patients.