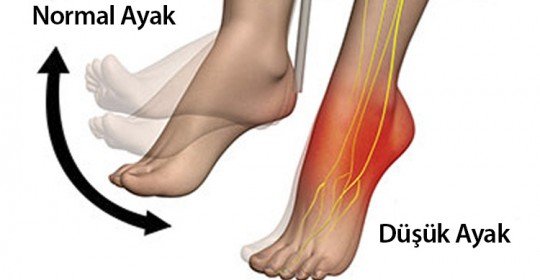
Inability to control the foot in different phases of walking due to different reasons (especially the loss of the ability to control the lifting of the foot from the ankle) is a clinical picture called drop foot. Since the person with low feet cannot lift his toes off the ground while walking, he drags his toes on the ground (Stepage gait), his normal gait is disrupted and his gait becomes uncontrolled. He/she may complain about his/her feet getting stuck somewhere, dragging his/her feet and not being able to walk fast, as well as it is difficult to go up and down hills and up and down stairs. They cannot walk in heels or slippers.
The normal foot is pulled upwards from the ankle, with proper functioning of the muscles and nerves, and stands at the midline to prepare for stance. Our systems that provide this movement of the foot are our nerves and muscles. It is the brain and spinal cord structure called the central nervous system that enables us to perform our normal movements voluntarily, and it converts the commands received from this system into normal movement with nerves leaving the spinal cord, healthy muscles and joints. Since a problem occurs in any of these structures in the low foot, healthy and normal walking is impaired, while the foot hangs down from the ankle and the person cannot pull it upwards even if he wants to.
Foot drop is a symptom, not a disease. First of all, the cause must be determined and the treatment for this cause must be determined. Drop foot may be the most important result of herniated disc, and the causes of “SILENT LOW FOOT” should also be examined.
Low foot clinical pictures that occur due to herniated disc, lumbar slippage, narrow canal in the waist and peripheral nerve traumas (such as nerve damage during injection from the hip) are called “painful drop foot” because they are accompanied by pain.
Multiple sclerosis, spinal cord traumas, brain cancers affecting the sciatic nerve, vein disease, diabetes, applying pressure by sitting on the knee for a long time in prayer and staying in the same position for a long time by putting a wallet in the back pocket are not accompanied by pain. It is responsible for the clinical picture we call “drop foot”.
In all kinds of clinical picture of drop foot, whether painful or not accompanied by pain, some shape and image distortions occur in the foot over time. The arch of the foot rises and the foot only touches the ground from the heel to the ground. Wounds or calluses occur due to changing pressures in various parts of the foot, and over time, calcification in the foot joints and deformities occur in the fingers. If not treated in time, swelling due to constant sprains and pain with movement may occur in the ankle region. If the necessary precautions are not taken, significant atrophy begins in the leg muscles on the side with the drop foot due to the drop foot.
These problems in the foot also negatively affect the movements of the knee and hip. Problems and pain may occur due to excessive stretching of the knee joint over time. Hip, back and waist pain may occur.
If this condition is not treated, it will be very difficult to treat these mechanical problems that will develop in the future.
If foot drop occurs due to nerve injury due to pathologies originating from the spine, the cause in the compression area should be surgically removed.
Ankle orthoses or supports (AFO) are most commonly used in the treatment of the disease. AFO is an orthosis worn on the foot and lower leg, usually made of plastic or lighter materials, and it supports the ankle at a 90 degree angle and helps walking by preventing the foot from being stuck on the ground. AFO cannot be worn with soft shoes, sandals or open-toed shoes. In addition, we should tell those around us that especially those with diabetes should not put pressure on their knees for a long time while praying or sitting on the ground.

